Introduction
| At a Glance | |
|---|---|
| Product | D-Link Xtreme N Storage Router (DIR-685) |
| Summary | 2.4 GHz Draft 11n router with slow built-in NAS, too-small front panel LCD photo display and very noisy little fan. |
| Pros | • Gigabit WAN and LAN w/ jumbo frame support • Wire-speed Gigabit routing • Wireless Guest zone • NAS performs better and has more features than other router NASes |
| Cons | • Fan screams like a banshee • Screen too small • FrameChannel won’t work behind another router • Membrane switch failed on review sample |
It’s not uncommon to find networking manufacturers adding unique features to their products in an effort to stand out from the crowd. The Linksys by Cisco WRT160NL, Belkin’s N+ as well as D-Link’s DIR-825 all include USB ports to convert an attached USB drive to networked storage. And Belkin created a bit of buzz when it introduced its N1 Vision almost two years ago with its front panel display.
So in its search for buzz and differentiation, D-Link has mashed together a single-band draft 802.11n router, BYOD NAS and Internet-connected digital photo frame into a small desktop package designed to make only a small footprint on your desktop. Unfortunately, some poor design decisions result in a product that we definitely recommend you take a pass on.
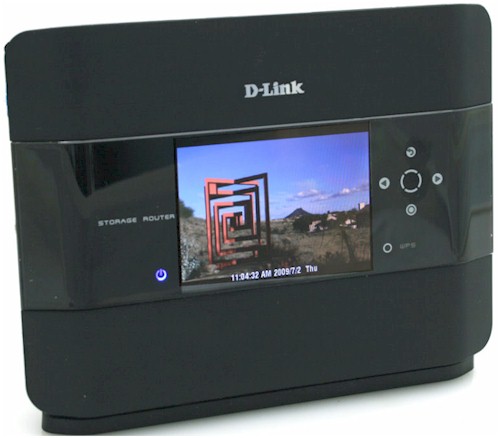
The 685 sits vertically in a weighted metal base and has a total depth that’s just slightly over 2.5”. The top tilts slightly towards the rear to provide a better viewing angle and to reduce glare on the screen.
Figure 1 shows the front panel. The four way touch pad with a center “select” button is used to navigate through the menus, which include six top level functions: Statistics; Status; WPS; Settings; Photos; and Frame Channel.
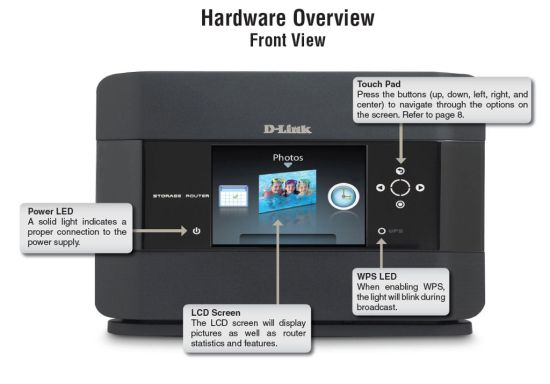
Figure 1: Front panel
The Status menu provides information about what’s going on inside your DIR-685. You can see LAN, WAN and WLAN status, status of the internal hard drive (if you’ve installed one), and general router information. Figure 2 shows general router status. Note that in the lower left corner the “Internet On” status shows that the 685 has a live internet connection.
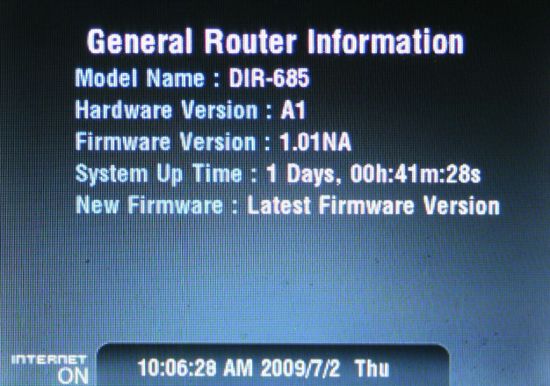
Figure 2: DIR-685 General Router Information displayed on the built-in LCD display
Figure 3 shows status of the internal 2.5" SATA hard drive that is up to you to buy and install.
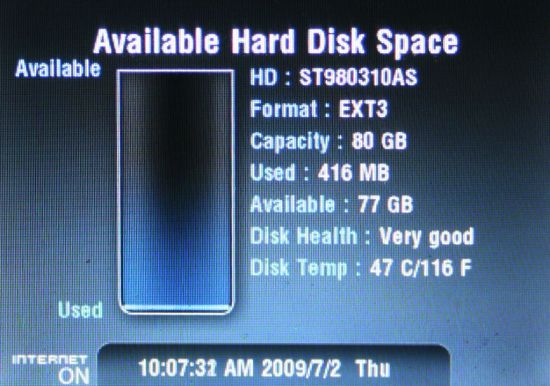
Figure 3: Hard Disk Status of the 2.5” SATA drive installed in the DIR-685
Figure 4 shows the rear panel of the DIR-685 with four switched Gigabit LAN ports and Gigabit Internet port, all of which are auto MDI/MDIX. Two USB ports allow you to add additional storage or connect to devices such as printers and scanners for the SharePort feature (more later). The Eject Button allows you to remove the drive (if installed). D-Link warns that you should dismount the drive by pressing the dismount button located below the drive door before ejecting the drive.
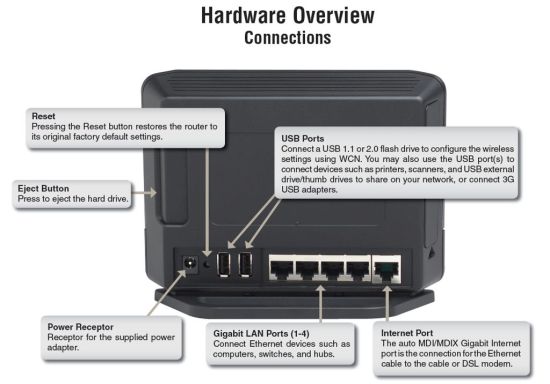
Figure 4: Hardware Overview – Rear Panel
On the Inside
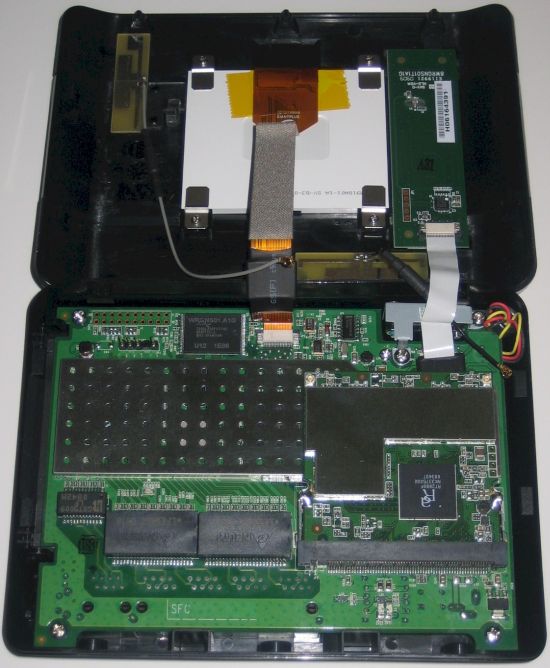
The 685’s 2×2 draft 802.11n radio uses a Ralink RT2880F 2T3R MAC/BB and RT2850L 2.4/5 GHz 2T3R transceiver. Though the radio is capable of dual-band operation, it is locked to single-band 2.4 GHz operation. The DIR-685 has 64 MB of RAM and 32 MB of flash. Figure 5 shows the internal layout of the DIR-685.
Figure 5: Internal Layout of the DIR-685
The WAN port and four LAN ports are handled by a Realtek RTL8366 Gigabit switch that appears to have support for jumbo frames up to 9K enabled. There is also a small, extremely loud fan that ran constantly during throughput and NAS testing. It sits at the top right of the case, in line with the radio and processor.
The processor could not be determined due to a soldered-in radio module over an RF shield. It does not appear Ubicom-based, however, since Ubicom’s signature automatic QoS features are not present in the 685. It does, however, support simpler QoS as shown in Figure 6.
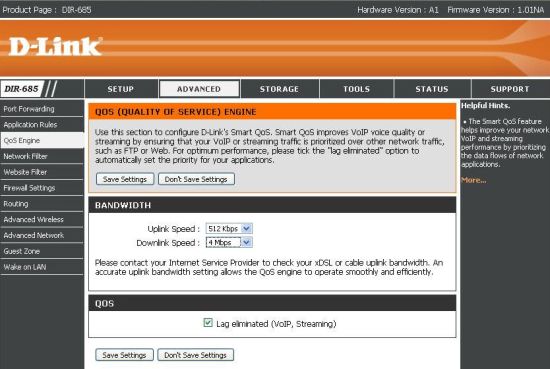
Figure 6: QsS Engine
Other D-Link routers automatically measure the uplink speed of your Internet connection to properly set QoS parameters. But you have to enter what you believe (or have tested) your Internet performance to be on the 685.
Setup
The 685’s setup is quite similar to other D-Link routers’. An adhesive label pasted across the ports on the rear of the router (that did not peel off cleanly) warns you to run the installation CD first. Of course, if you have a Mac, you’re out of luck – the wizard is only PC-Based. D-Link does, however, provide a large 28” X 15” setup poster that will guide you through a basic installation – regardless of what type of computer you’re using.
The PC-based wizard gives you the option of using the DIR-685 as a replacement router, or to use it in addition to your existing router. I chose the second option, since I planned to test the router “behind” my existing DIR-655. The wizard guides you through all of the steps required to set up your router, including unplugging and plugging in cables.
Since I have installed dozens of routers, I skipped ahead and made all of the wiring changes required before running the wizard. That turned out to be a mistake, as the wizard thought that my Ethernet cable was disconnected – even though it was connected and had already gotten an IP address from the 685. I disconnected everything and re-ran the wizard, carefully following each step without jumping ahead, and the wizard did completely configure the router – including setting up the wireless network security and administrator password.
It’s worth noting that the wizard instructs you to plug in your cables based on color-coded ports – blue for LAN and gray for Internet. Though it may be limited to the first production run of the 685, none of the ports on my review unit were color coded like other D-Link products I’ve reviewed. The ports were identified, however, with numbers and “WAN” molded into the plastic and a small label on the rear panel.
My recommendation would be that if you’re tech-savvy enough to connect your modem and computer to the WAN and LAN ports, go ahead and do so and skip the "wizard". After rebooting your modem and router, point the browser on the computer connected to the LAN port to http://192.168.0.1. It will save you a lot of time. A wizard in the router runs the first time you connect to it.
Hands On
If you’re familiar with D-Link products, the user interface will look almost identical to what you’ve seen in other gear. You can hit D-Link’s online emulator to explore at your leisure. I’ll just hit a few points here.
If you already own a D-Link NAS like the DNS-323, you’ll feel right at home. Figure 7 shows the Disk Management page.
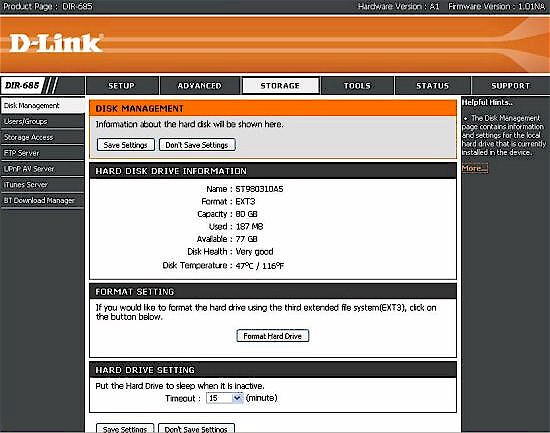
Figure 7: Disk Management
Like other D-Link NASes, the 685 includes UPnP AV and iTunes servers, a basic FTP server as well as a BitTorrent download manager. It also supports user and group creation for folder access control. You can set access to shares by user or group or just leave the volume “open” to be shared by all users with read/write access.
The FTP server supports anonymous access or you can set directory access and R/W privileges separately. The built-in iTunes server worked as expected, and the 685 showed up in iTunes as a shared resource. One item noticeable omission is the ability to set a Windows workgroup, which is set as workgroup.
As a router, there’s not too much to mention – for the most part, it parallels the features found in the DIR-825. You have a full complement of port forwarding, Application Rules, Network Filtering, Website Filtering and Firewall rules as shown in Figure 8.

Figure 8: Advanced routing features
D-Link kept the DHCP reservation feature – something that I personally use on my network at home. It allows you to reserve a specific IP address for an individual host based on MAC address. This is useful if you have a number of NASes or other devices like managed switches that you want to stay at known IP addresses. This saves you the hassle of assigning a static IP address for them.
As a security feature, the DIR-685 also supports CAPTCHA-style graphical authentication as shown in Figure 9. This feature was recently rolled out across many of D-Link’s routers and is intended to protect your router from “bot” attacks should you have remote management enabled. This feature is enabled by default, but you can choose to disable it.
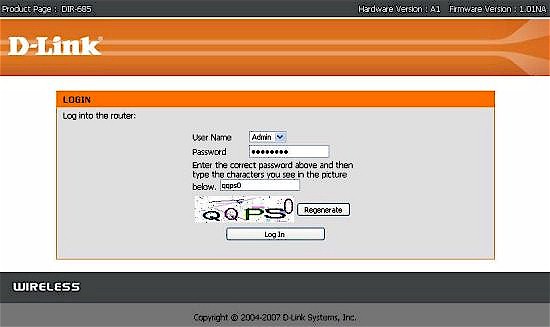
Figure 9: Login page with graphical authentication
FrameChannel
If you had to choose a defining feature of the 685, it would have to be the color front panel display. In addition to displaying router status information and providing access to some configuration features, it can display a slideshow of photos from the internal hard drive or content from D-Link’s partner FrameChannel service.
D-Link partnered with Frame Media around the beginning of 2008, when it launched its D-Life product line. The FrameChannel service provides access to Internet content such as photo-sharing sites, RSS feeds, news, and yes, even your Twitter account “tweets” directly to ‘net-connected devices like photo frames and now, the screen on the 685. For a major feature, however, it’s not very well documented – the first mention of it appears on page 96 of the CD-based user guide, and at the bottom of the quick install poster.
To set it up, with an active Internet connection, you scroll over to the FrameChannel icon on the router and hit the center key. A five digit activation key appears. Next, you navigate to http://D-Link.framechannel.com and create an account. Don’t worry – it’s free. Once you create your account, you enter the activation code found on the LCD of the 685 and it links your DIR-685 to your FrameChannel account.
From your online account, you can select the news feeds, photos and photo sharing sites (FrameChannel supports sites such as Picasa, Facebook and Flickr) you want to appear on your screen. Once you’ve chosen your content, you can choose to preview how the content will appear on your screen as shown in Figure 10.
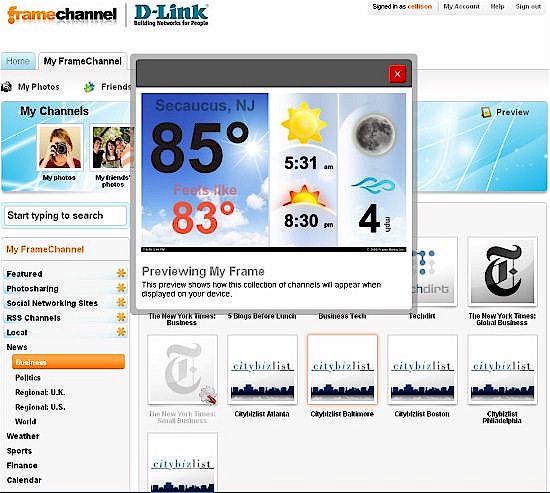
Figure 10: FrameChannel screen preview
It’s just that simple – or at least it should be. In my network configuration, ie, the 685 behind another router (an allegedly supported configuration), I was unable to get the FrameChannel feature to work at all. After several calls and emails with D-Link, I concluded that the problem must be related to having an additional NAT router / firewall between the 685 and Internet. Because when I plugged in the DIR-685 directly into my cable modem, it worked exactly as advertised. All of the content that I had configured in my account at the FrameChannel started to appear on the 685’s screen – exactly as previewed.
D-Link claimed that my configuration wasn’t very common, but I’m not so sure. Many DSL ISPs actually include a router in their DSL modems (or at least a NAT firewall) and provide a private IP address for connection to a router’s WAN port. This is essentially the setup that I had, except I connected the 685’s WAN port to one of my main router’s LAN ports. Either way, D-Link has confirmed that this doesn’t work and may address it in a future firmware update.
As I mentioned earlier, the 685 also lets you generate a slide show from photos that are stored on the drive mounted inside the router. You use the front panel keypad, navigate to the folder containing the photos you would like to display and hit the “center” key to confirm. A slideshow of the images in your selected directory will then start to play. Unlike most photo frames, however, you can’t rotate photos, nor can you change transitions between the slides, or, for that matter, the length of time between slides.
SharePort
The DIR-685 has two rear panel USB ports that support D-Link’s SharePort feature. Shareport allows one-at-a-time networked access to USB devices such as printers and storage devices from Windows or Mac OS X systems running a SharePort utility. In addition to running the utility, all drivers for the shared device must also be pre-installed on the computer that will be using it.
We covered SharePort technology extensively in the DIR-825 review, so I won’t cover it again. Suffice it to say that I prefer the USB storage sharing found on most other NAS products. For those products, no driver or other software is required, and multiple users can map to the attached USB storage device as another share on the NAS.
Figure 11 shows the SharePort utility with two attached USB storage devices attached to the local computer. Drives F and G are the USB devices and appear as local drives.
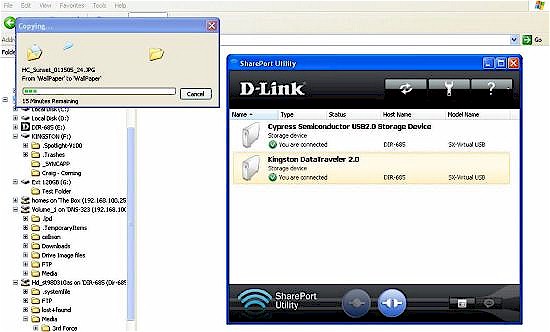
Figure 11: SharePort Utility showing two USB drives
Routing Performance
Testing and analysis by Tim Higgins
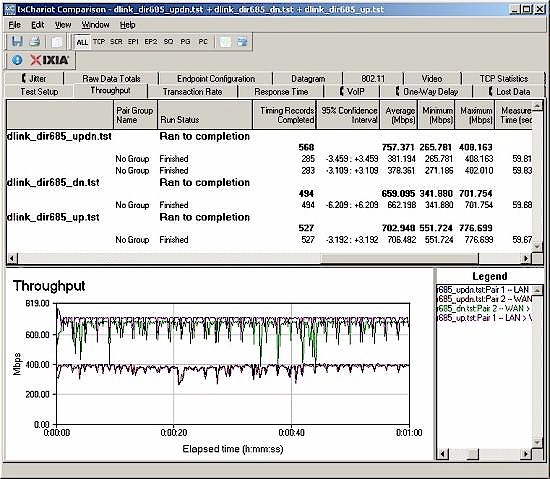
Routing performance for the 685 using our standard test method is summarized in Table 1. The 685 delivered an unprecedented 659 Mbps of downstream throughput and 703 Mbps upstream. I frankly didn’t believe these numbers and triple checked the results and they appear to be real.
I have no idea who can take advantage of such extreme throughput. But if you do, please note that the front panel LCD will break up and go crazy if you actually run at even around 100 Mbps. The router doesn’t lock up, however.
| Test Description | DIR-685 Throughput – (Mbps) |
|---|---|
| WAN – LAN |
659
|
| LAN – WAN |
703
|
| Total Simultaneous |
757
|
| Maximum Simultaneous Connections | 200 |
| Firmware Version |
1.01NA
|
Table 1: Routing test results
Figure 12 is a composite plot of the three routing tests, which shows pretty steady routing throughput. If you check the Router Charts you’ll see that the 685 sits comfortably at the top.
Figure 12: Routing throughput composite plot
NAS Performance
Testing and analysis by Tim Higgins
I ran a quick check of the 685’s NAS performance using both iozone and Vista SP1 file copy methods. Figure 13 shows the iozone results, which are around 5 – 6 MB/s after cache effects die out at the larger file sizes.
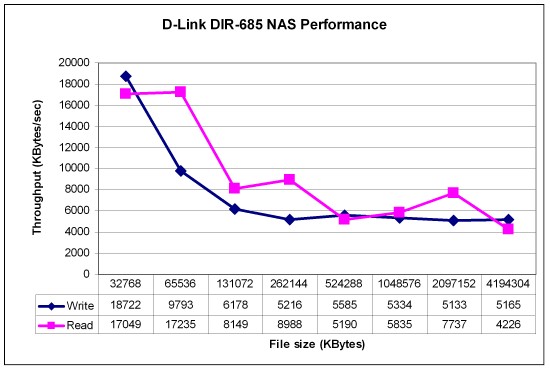
Figure 13: iozone NAS throughput
Vista file copy tests showed 4.85 MB/s for write, but a surprising 11.2 MB/s for read. The 5 MB/s is slightly better than I have seen with other router USB-drive sharers and the read performance is around 2X better. But neither will make you happy if you’re moving a lot of big files around or doing large backups.
Wireless Features
The wireless features of the DIR-685 are essentially the same as on D-Link’s other single-band draft 11n routers. Figure 14 is the Basic Wireless settings page, which contains the familiar set of D-Link wireless controls. Scheduled wireless enable, SSID, 802.11 Mode, Auto channel selection, Channel select, Transmission rate and Channel Width, Short Guard Interval, WMM Enable and SSID Broadcast Disable are all there.
D-Link has been trying to back away from supporting 802.11b in its draft 11n routers and the product data sheet makes no mention of 802.11b support. But the 802.11 Mode selector includes it among the 802.11g Only, Mixed 802.11g and 802.11b, 802.11b Only, 802.11n Only, Mixed 802.11n, 802.11b and 802.11g and Mixed 802.11n and 802.11g modes supported.
Figure 14: Basic wireless settings
The 685 supports manual setup for wireless security with WEP, WPA, WPA2 and mixed WPA/WPA2 options. Also supported are the Consumer and "Enterprise" (RADIUS) forms of WPA/WPA2, which are selected via the slightly obfuscated PSK/EAP switch.
There is also a wizard to walk you through wireless setup, allowing you to name your wireless network and set security settings. The wizard permits No security (not recommended) WEP, or WPA.
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) is also supported to make enabling a secure connection very easy—as long as your client also supports WPS. Tim was able to complete a WPS PIN session using the Intel Wi-Fi Link 5300 client that resulted in a WPA2/ AES secured connection.
I was glad to see that the 685 supports a wireless Guest Zone (Figure 15). The Guest Zone creates an entirely different subnet for wireless "guests" to provide Internet access. It has its own SSID, DHCP server, MAC address filtering and wireless security. You can also control wireless client-to-client communication and routing between the Guest Zone and your LAN and WLAN.
Figure 15: Wireless Guest Zone
Figure 16 shows the Advanced Wireless settings, the most useful of which is Transmit Power. The Short Guard Interval control would also be more at home on this page.
Figure 16: Advanced wireless settings
Wireless Performance
Testing and analysis by Tim Higgins
I used the open air test method described here to test the 685’s wireless performance. Testing was done using the SNB standard wireless test client, an Intel Wi-Fi Link 5300 AGN mini-PCIe card and 12.2.0.11 driver in a Dell Mini 12 running WinXP Home SP3. I left all client-side defaults in place except for enabling throughput enhancement (packet bursting) and changing the 802.11n Channel Width (2.4 GHz) setting from its 20 MHz default to Auto, so that the adapter would support 40 MHz channel bonding mode.
The router had the latest 1.01NA firmware and all factory default settings in place, except setting channel 1.
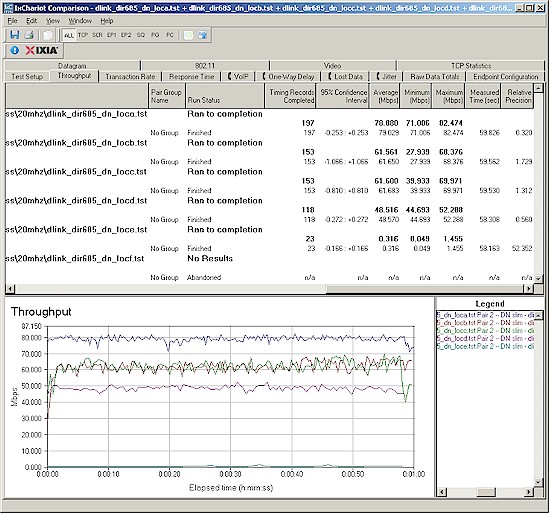
Figure 17 shows a composite of up and downlink throughput tests made at the six test locations with both 20 and 40 MHz channel width modes. Each column represents the average throughput from a one minute test. Best case throughput of 111.4 Mbps was measured running downlink with a 40 MHz channel bandwidth at Location A.
Unfortunately, the 685’s range performance isn’t a match for its peak speed. Unlike most other 2.4 GHz draft 11n routers that I have tested lately, the 685 was unable to run the throughput tests in the most difficult Location F and barely made it through the tests in Location E. So if you’re looking for long range in a draft 11n router, the 685 probably isn’t a good choice.
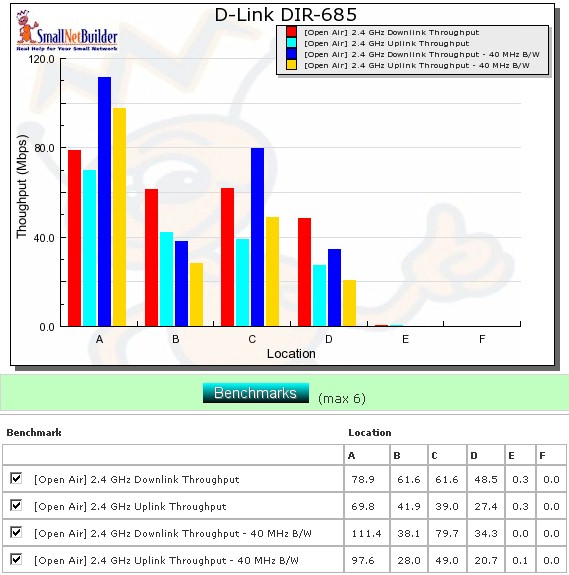
Figure 17: Six location wireless throughput summary
The good news, however is that the IxChariot plot in Figure 18 shows much lower throughput variation than I am accustomed to seeing from draft 802.11n routers.
Figure 18: Six location wireless throughput – 2.4 GHz, 20 MHz channel, downlink
If you’d like to see the other IxChariot plots just click the links: 20 MHz uplink, 40 MHz downlink, 40 MHz uplink.
Wireless Security
Figure 19 shows that the 685 properly (as per draft 802.11n standard requirements) limits performance to 11g speeds with WEP and WPA/TKIP enabled. And selecting WPA2/AES security has no significant effect on throughput.
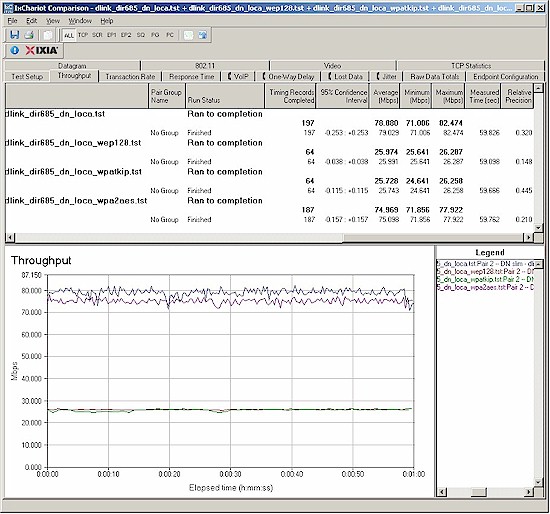
Figure 19: Security mode comparison – 2.4 GHz, 20 MHz channel, downlink
Wireless Performance – Competitive Comparison
The 685 doesn’t really have any comparable competitors, so for comparison, I just chose two other single-band draft 11n routers with Gigabit switches that have also been tested using the Intel 5300 client: the Linksys WRT310N and D-Link DIR-655 [A4].
Figure 20 shows a comparison of downlink, 20 MHz bandwidth mode tests. The 685 actually does quite well in the strong to medium signal level locations A – D. But it drops out of the competition in the low signal locations E and F.
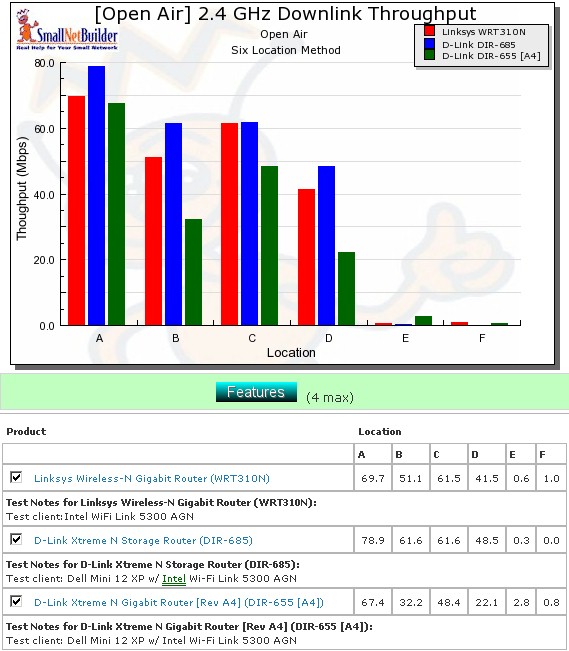
Figure 20: Competitive comparison – 2.4 GHz, 20 MHz channel, downlink
Table 2 summarizes the highest downlink throughput product in each location for the two modes tested and Table 3 compares uplink results. The chart was generated by going through the six-location comparison plots and putting an X in the product’s box that had the highest throughput for each test. If values are within 0.5 Mbps of each other, they each get an "X".
| Product | 2.4GHz /20 | 2.4GHz / 40 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| Linksys WRT310N | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| D-Link DIR-685 | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| D-Link DIR-655 [A4] | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||
Table 2: Best downlink throughput summary
Adding up the checkmarks for each product shows all three products tied for overall performance running downlink. But the DIR-655 [A4] is clearly the winner running uplink. I do have to say, however, that for strong to medium signal level Locations A-D, the DIR-685 consistently beats the other two products.
| Product | 2.4GHz /20 | 2.4GHz / 40 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| Linksys WRT310N | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| D-Link DIR-685 | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| D-Link DIR-655 [A4] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
Table 3: Best uplink throughput summary
Use the Wireless Charts to generate other comparisons.
Closing Thoughts
D-Link simultaneously broke new ground and took a chance with the introduction of the DIR-685. Will this combined, “mashed-up” appliance with router, NAS and photo frame functions be the precursor to similar products or will it be relegated to the category of “nice idea, but it didn’t work out”?
On the plus side, I like having all of the features combined into a single piece of hardware that takes up less space in my office, and arguably takes less power than individual components. But after working with the DIR-685 for more than a week, I’ve decided that it’s not going to replace my DIR-655.
You might assume that my experience with FrameChannel not working behind a second router would be the reason, but you’d be wrong. My reasons for not recommending the 685 are:
- The screen is too small – A 3.2” screen might be fine for occasionally checking router statistics or the status of the internal hard drive, but it’s just too small for displaying photos, or for that matter, text from RSS feeds. If you really want internet photo sharing, a much better choice would be D-Link’s DSM-210, a 10” photo frame that employs the same FrameChannel technology found in the 685. Granted, it sells for almost as much as the 685, but the images on it are large enough that you don’t have to be sitting a few feet away to enjoy them.
- The fan is way too noisy – While many routers spend their lives stuck behind equipment in a closet near a cable/DSL modem, the whole idea of the DIR-685 is for it to sit on your desk where you can view it. It doesn’t take much of a load on the device for the fan to come on, and when it does, you’ll want to smother it with a pillow. This reason alone is enough to kill any desire I might have had to own the product.
- Poor thermal design – The fact that a small, very noisy fan had to be used to cool the 685, speaks volumes for the thermal design (or lack thereof) of the product. Although the design won a “Red Dot” design award in Europe, nice looks are one thing and appropriate-for-use design are another. D-Link did not choose wisely when it chose form over function.
- Reliability – It’s unual for a product to break during the gentle handling that it receives during review, but that’s what happened with the 685’s front panel keypad. It’s bad enough that the membrane-type switch has no tactile or audible feedback. But by the end of a week or so of light use, it appeared that one of the switch locations (the WPS key) seemed to be permanently pressed. With the WPS message permanently fixed on the screen, none of the other keys were operational, and I could no longer access other front panel functions.
- Remote Access – D-Link is behind the competition when it comes to remote access to files stored on the optional internal drive. Other manufacturers such as Buffalo and Seagate provide nice, web-based remote access to your files based on user access permissions. D-Link’s solution it the same as it has been for years – you access your files via a built-in FTP server. While the FTP server does provide remote file access, the browser-based secure remote file access offered by competing NAS products is a superior solution.
D-Link deserves high marks for developing an innovative, “all-in-one” product targeted at the home office. And while I like many of the features of the DIR-685, it’s still very much a “1.0” product. I’m sure that it will appeal to buyers who want the combined features all in a single package and don’t mind an annoyingly loud fan. But I’ll wait for a future version, if there is one, which is quieter, and has a larger screen.